Code
#include "stdafx.h"
#include <stdio.h>
#include <conio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
//initializing the memory and registers
void initialization(int a[]){
for(int i=0;i<16;i++)
a[i]
= (i+1)*10;
}
//number of instructions
int input_instructions(){
int x;
printf("Enter the number of instructions
you want to perform: ");
scanf_s
("%d",&x);
return x;
}
//loading the register from memory
void load(int row, int inst[][3]){
inst[row][0]
= 1;
printf("Enter the number of register
ranging from 1 to 16: ");
scanf_s("%d",&inst[row][1]);
printf("Enter the number of memory from
which you want to load ranging from 1 to 16: ");
scanf_s("%d",&inst[row][2]);
}
//adding the two registers
void add(int row,int inst[][3]){
inst[row][0]
= 5;
printf("Enter the destination register
number: ");
scanf_s("%d",&inst[row][1]);
printf("Enter the source register number:
");
scanf_s("%d",&inst[row][2]);
}
//storing the value to the memory
void store(int row,int inst[][3]){
inst[row][0]
= 3;
printf("Enter the register number: ");
scanf_s("%d",&inst[row][1]);
printf("Enter the memory number: ");
scanf_s("%d",&inst[row][2]);
}
//display the instruction memory
void display_pattern(int no_of_ins,int inst[][3]){
system("cls");
printf("\********************************************************************************");
printf("\n******************************
Instruction Memory ******************************");
printf("\n********************************************************************************");
for(int i=0;i<no_of_ins;i++){
printf("\n\t\t\t\t%d\t%d\t%d\n",inst[i][0],inst[i][1],inst[i][2]);
}
printf("\n\n");
for(int i=0;i<no_of_ins;i++){
if(inst[i][0] == 1){
printf("\t\t\t\tLoadR\tR%d\tM%d\n\n",inst[i][1],inst[i][2]);
}
else if(inst[i][0] == 3){
printf("\t\t\t\tStoreR\tR%d\tM%d\n\n",inst[i][1],inst[i][2]);
}
else if(inst[i][0] == 5){
printf("\t\t\t\tAddR\tR%d\tR%d\n\n",inst[i][1],inst[i][2]);
}
}
printf("\n\n\n\nPress any key to
continue...");
_getch();
}
//display registers and memorys
void display_reg_mem(int reg[],int mem[]){
printf("\n\nRegister: ");
for(int j=0;j<16;j++)
printf("%d
",reg[j]);
printf("\n-----------------------------------------------------------------------------");
printf("\nMemory: ");
for(int j=0;j<16;j++)
printf("%d
",mem[j]);
}
//ISA simulator
void display_cycles(int no_of_inst,int inst[][3],int reg[],int mem[]){
for(int i=0;i<no_of_inst;i++){
system("cls");
printf("********************************************************************************");
printf("\n******************************
ISA Simulator ***********************************");
printf("\n********************************************************************************");
printf("\n\n\n\n\n*******************************
Instruction # %d ********************************",(i+1));
printf("\n\n\n\n\nFetch Instruction:\t
%d\t%d\t%d\n",inst[i][0],inst[i][1],inst[i][2]);
display_reg_mem(reg,mem);
if(inst[i][0] == 1){
printf("\n\n\n\n\nDecode Instruction:\t
LoadR\tRegister%d\tMemory%d\n",inst[i][1],inst[i][2]);
display_reg_mem(reg,mem);
printf("\n\n\n\n\nExecute Instruction:\t
Register updated Succesfully\n");
reg[(inst[i][1]-1)]
= mem[(inst[i][2]-1)];
display_reg_mem(reg,mem);
}
if(inst[i][0] == 5){
printf("\n\n\n\n\nDecode Instruction:\t
AddR\tRegister%d\tRegister%d\n",inst[i][1],inst[i][2]);
display_reg_mem(reg,mem);
printf("\n\n\n\n\nExecute Instruction:\t
Register updated Succesfully\n");
reg[(inst[i][1]-1)]
= reg[(inst[i][1]-1)] + reg[(inst[i][2]-1)];
display_reg_mem(reg,mem);
}
if(inst[i][0] == 3){
printf("\n\n\n\n\nDecode Instruction:\t
StoreR\tRegister%d\tMemory%d\n",inst[i][1],inst[i][2]);
display_reg_mem(reg,mem);
printf("\n\n\n\n\nExecute Instruction:\t
Memory updated Succesfully\n");
mem[(inst[i][2]-1)]
= reg[(inst[i][1]-1)];
display_reg_mem(reg,mem);
}
printf("\n\n\n\nPress any key to
continue...");
_getch();
}
}
int main(){
system("color 3f");
int choice,count=0,row=0,lines;
int registers[16] = {0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0};
int memorys[16];
initialization(memorys);
lines
= input_instructions();
int instructions[100][3];
for(int i=0;i<lines;i++){
system("cls");
printf("Select one of the following
instruction type from the following:\n");
printf("\t1. Load \n");
printf("\t2. Add \n");
printf("\t3. Store \n");
printf("\t4. Exit \n\n");
printf("Enter your choice: ");
choice
= _getche();
switch (choice)
{
case '1': //load
system("cls");
load(row,instructions);
row++;
break;
case '2': //add
system("cls");
add(row,instructions);
row++;
break;
case '3': //store
system("cls");
store(row,instructions);
row++;
break;
case '4': //exit
exit(0);
default:
system("cls");
printf("\n\nInvalid input! Press any key to
continue.");
break;
}
}
system("cls");
display_pattern(lines,instructions);
system("cls");
display_cycles(lines,instructions,registers,memorys);
exit(0);
return 0;
}
Program Output - Screen Shots
In
the above screen 01 user must enter the instructions to run the program. For
example we want to run our code for 4 instructions, so we will write 4 and hit
enter.
The following screen will
be displayed.
There
are 4 options 1st option is used to load the register from memory, 2nd
option add the two registers, 3rd option stores the value from
register to the memory, and the 4th option is used to quit the
program. For example, we press 1 and hit enter.
The following screen will
be displayed.
User
will be asked to enter the register number and the memory number. We will enter
2 for register and 7 for memory.
Same procedure will be
followed again i.e. steps for screen 02.
This time we will enter 3
for register and 6 for the memory.
After
you have entered the value in the memory hit enter… the program will show you
the following screen.
This time press 2 and hit
enter.
It
will ask you to enter two register numbers one by one. The 1st
register is the destination and the 2nd register is the source i.e.
after the value is entered, the value of the destination will be overwritten with
the sum of the two registers in the add
instruction. Here we have entered 2 and 3 register numbers where 2nd
register will be overwritten after the execution with the sum of the register
no 2 and 3.
After you enter the
register number, the above screen will be displayed again, press 3 this time
and hit enter.
The above screen will be
shown asking the user to enter the register number from which he/she wants to
store data and then the program will ask for the memory number. For instance,
we enter 2 for register and 6 for memory and press enter.
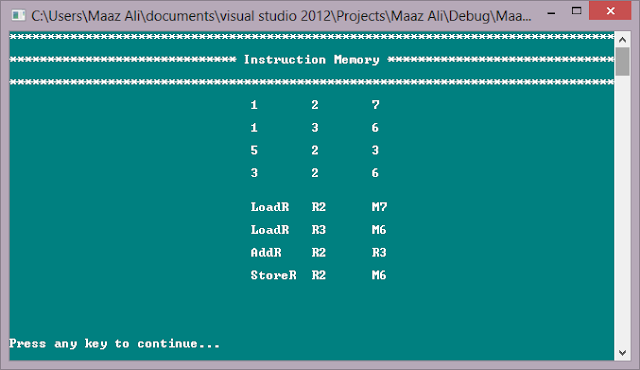
As, we have entered 4
instructions (2 load, 1 add and 1 store). The above screen will be displayed
asking the user to press any key to continue if he/she have viewed the
instructions. After we hit enter the following screen will be displayed.
The
program will show the user ISA simulator with the 1st instruction.
As, the 1st instruction was to load the register from the memory
i.e. 1 2 7. After the execution the register’s value will be updated and as we
can see in our example it has updated the 2nd register with the
value 70 taken from the memory’s 7th location.
Let’s
have a closer look at the above screen 11, we can see there are three steps
involved are involved for each cycle (instruction).
1st step - the fetch instruction
It
fetches the instruction from the memory and loads it into the processor.
2nd step - the decode instruction
After
the 1st step the 2nd step takes place: It decodes the
instruction after it has been fetched, so that the computer can perform its
specific operation.
3rd step - execute instruction
It
executes the instruction and updates the values according to the instruction,
for instance in this instruction it will update the value of the 2nd
register.
Similarly
2nd instruction will be displayed. It will update the 3rd
register with the value 60.
The
third instruction was to add the 2nd and 3rd register and
answer have to be stored in the 2nd register as it was the
destination register. Hence, we can see the value of the 2nd
register have been updated to 130 from 70.
The
last and 4th instruction that we entered was to store the result of add
instruction from the 3rd instruction to the memory. In the above
example we have stored the value of the 2nd register in the 6th
memory location.
The
user will be asked to press any key to continue and the program will be
terminated as there were no more instructions to show.





















.png)





No comments :
Post a Comment
Note: Only a member of this blog may post a comment.